MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline入门
MongoDB 的 Aggregation Pipeline 是处理和分析数据的强大工具,适用于实时查询和离线数据分析。它允许开发者使用多个阶段(stages)来转换、过滤、分组和排序数据,从而高效地执行复杂的计算。本文将探讨 Aggregation Pipeline 的基本概念、应用示例、性能分析及优化方案。
Aggregation Pipeline 基础
Aggregation Pipeline 由多个 stage 组成,每个 stage 负责特定的数据处理任务,例如:
$match:用于筛选文档,类似 SQL 的WHERE,用于减少数据扫描量。例如,SELECT * FROM orders WHERE status = 'active';相当于{ "$match": { "status": "active" } }。$group:对数据进行分组并计算聚合值,类似 SQL 的GROUP BY。例如,SELECT category, COUNT(*) FROM orders GROUP BY category;在 MongoDB 中可用{ "$group": { "_id": "$category", "count": { "$sum": 1 } } }实现。$sort:对数据进行排序,类似 SQL 的ORDER BY,例如SELECT * FROM orders ORDER BY createdAt DESC;相当于{ "$sort": { "createdAt": -1 } }。$project:调整字段输出,类似 SQL 的SELECT column1, column2 FROM table;,在 MongoDB 中可用{ "$project": { "name": 1, "price": 1 } }。$lookup:进行表关联(类似 SQL 的JOIN),例如 SQL 的SELECT * FROM orders INNER JOIN customers ON orders.customerId = customers.id;在 MongoDB 中可用{ "$lookup": { "from": "customers", "localField": "customerId", "foreignField": "_id", "as": "customer" } }。$unwind:将数组字段展开,相当于 SQL 的LATERAL VIEW,用于处理嵌套数据。$merge:将结果写入新的集合,类似于 SQL 的INSERT INTO new_table SELECT * FROM old_table;。
下面是一个Aggregation的示例,筛选所有status为active的文档,然后按照
category
进行分组,并计算每个类别中的文档数量,最后按照数量从高到低排序,返回每个类别及其对应的
active 记录数。
[
{ "$match": { "status": "active" } },
{ "$group": { "_id": "$category", "count": { "$sum": 1 } } },
{ "$sort": { "count": -1 } }
]Aggregation应用场景
实时数据分析与监控
在许多业务场景中,企业需要对实时数据进行监控和分析,以便快速做出决策。例如,在电商平台中,分析用户的实时访问数据可以帮助优化推荐系统,而在金融行业,监控交易数据可以用于欺诈检测。
Aggregation Pipeline 允许开发者构建高效的数据流处理系统。例如,利用
$match 过滤特定交易类型,结合 $group
计算统计指标,可以实时监控异常交易。例如:
[
{ "$match": { "transactionAmount": { "$gt": 10000 } } },
{ "$group": { "_id": "$userId", "totalSpent": { "$sum": "$transactionAmount" } } },
{ "$sort": { "totalSpent": -1 } }
]这个 Aggregation Pipeline 可以实时监测高额交易,并排序用户的消费情况,有助于发现可疑交易行为。
数据ETL与预聚合
对于数据仓库和大数据分析场景,Aggregation Pipeline 可以用于数据抽取(ETL)和预聚合处理,减少查询开销,提高性能。例如,社交媒体平台可能需要分析用户的历史行为数据,以生成个性化推荐。
一个典型的 ETL 任务可能包括:
- 使用
$lookup连接多个集合的数据,如用户行为日志和商品信息。 - 过滤无效数据,减少存储压力。
- 通过
$group进行聚合计算,生成预计算的数据表。 - 使用
$merge将数据存入新的集合,以便后续查询。
[
{ "$match": { "eventType": { "$in": ["click", "purchase"] } } },
{ "$group": { "_id": "$userId", "interactions": { "$push": "$eventType" } } },
{ "$merge": "user_behavior_summary" }
]通过这样的 Aggregation Pipeline,企业可以提前计算用户的行为特征,减少在线查询时的计算压力,提升查询性能。这种方式特别适用于大规模数据处理,如推荐系统、广告投放优化和用户行为分析。
Aggregation使用示例
本节我们将使用一个完整的示例来展示Aggregation的用法。
数据准备
在开始演示 Aggregation 之前,我们需要准备一个示例数据库
sales_db,其中包含一个 orders
集合,结构如下:
{
"order_id": 1,
"customer": "Alice",
"items": [
{ "product": "Laptop", "price": 1000, "quantity": 1 },
{ "product": "Mouse", "price": 50, "quantity": 2 }
],
"total": 1100,
"date": ISODate("2024-03-10T10:00:00Z")
}使用mongoshell插入一些示例数据(包括orders和customers
collection):
> use sales_db
> db.orders.insertMany([
{
"order_id": 1,
"customer": "Alice",
"items": [
{ "product": "Laptop", "price": 1000, "quantity": 1 },
{ "product": "Mouse", "price": 50, "quantity": 2 }
],
"total": 1100,
"date": new ISODate("2024-03-10T10:00:00Z")
},
{
"order_id": 2,
"customer": "Bob",
"items": [
{ "product": "Monitor", "price": 300, "quantity": 1 },
{ "product": "Keyboard", "price": 80, "quantity": 1 }
],
"total": 380,
"date": new ISODate("2024-03-12T14:30:00Z")
},
{
"order_id": 3,
"customer": "Charlie",
"items": [
{ "product": "Tablet", "price": 500, "quantity": 1 },
{ "product": "Headphones", "price": 100, "quantity": 2 }
],
"total": 700,
"date": new ISODate("2024-03-15T09:45:00Z")
},
{
"order_id": 4,
"customer": "David",
"items": [
{ "product": "Smartphone", "price": 900, "quantity": 1 },
{ "product": "Charger", "price": 30, "quantity": 1 }
],
"total": 930,
"date": new ISODate("2024-03-18T12:10:00Z")
},
{
"order_id": 5,
"customer": "Alice",
"items": [
{ "product": "Laptop", "price": 1200, "quantity": 1 },
{ "product": "Mouse Pad", "price": 20, "quantity": 1 }
],
"total": 1220,
"date": new ISODate("2024-03-20T15:30:00Z")
}
]);
> db.customers.insertMany([
{ "_id": 1, "name": "Alice", "email": "alice@example.com", "phone": "123-456-7890" },
{ "_id": 2, "name": "Bob", "email": "bob@example.com", "phone": "234-567-8901" },
{ "_id": 3, "name": "Charlie", "email": "charlie@example.com", "phone": "345-678-9012" },
{ "_id": 4, "name": "David", "email": "david@example.com", "phone": "456-789-0123" }
]);插入数据后,用MongoDB Compass查看: 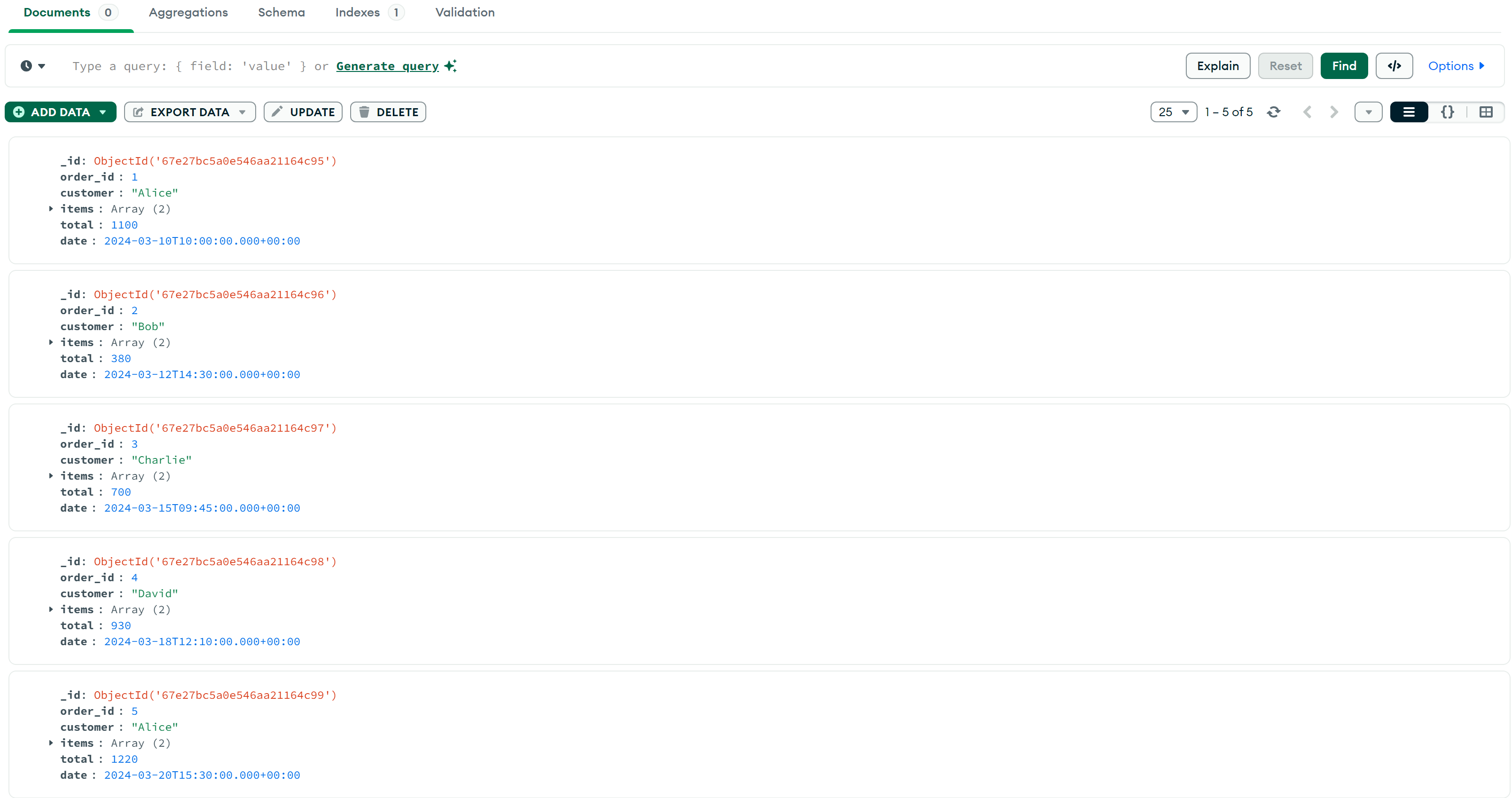
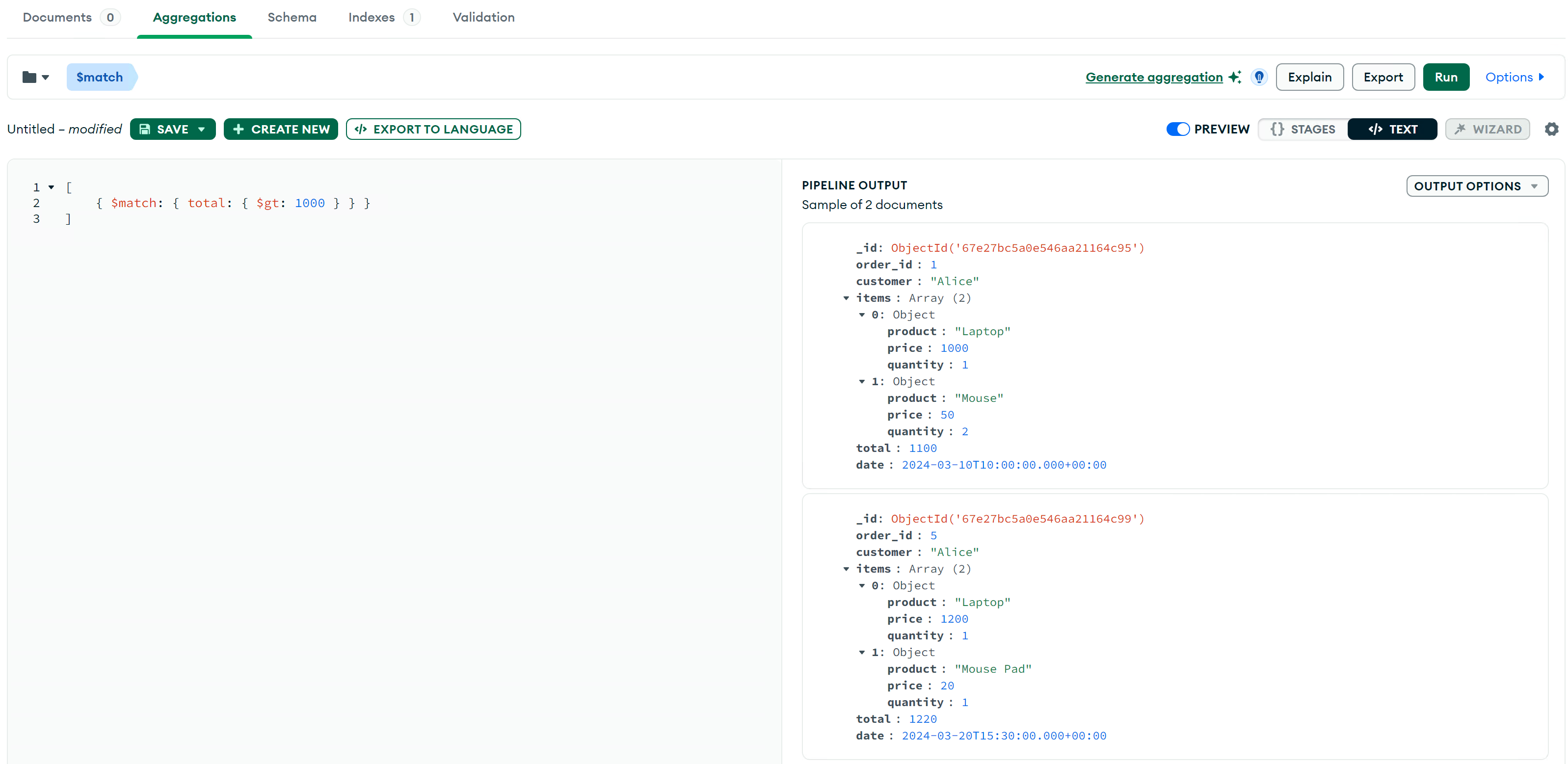
$match 筛选数据
获取 total 大于 500 的订单:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $match: { total: { $gt: 1000 } } }
]);在Compass中的Aggregations Tab的执行结果(注意只使用括号内的内容):
$group 分组计算
按客户分组,计算每位客户的总消费金额:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$customer", total_spent: { $sum: "$total" } } }
]);结果:
{
"_id": "Bob",
"total_spent": 380
}
{
"_id": "Charlie",
"total_spent": 700
}
{
"_id": "Alice",
"total_spent": 2320
}
{
"_id": "David",
"total_spent": 930
}$sort 排序
按客户总消费金额降序排列:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$customer", total_spent: { $sum: "$total" } } },
{ $sort: { total_spent: -1 } }
]);结果:
{
"_id": "Alice",
"total_spent": 2320
}
{
"_id": "David",
"total_spent": 930
}
{
"_id": "Charlie",
"total_spent": 700
}
{
"_id": "Bob",
"total_spent": 380
}$project
选择和修改字段
只显示订单号、客户和总金额:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $project: { _id: 0, order_id: 1, customer: 1, total: 1 } }
]);结果:
{
"order_id": 1,
"customer": "Alice",
"total": 1100
}
{
"order_id": 2,
"customer": "Bob",
"total": 380
}
{
"order_id": 3,
"customer": "Charlie",
"total": 700
}
{
"order_id": 4,
"customer": "David",
"total": 930
}
{
"order_id": 5,
"customer": "Alice",
"total": 1220
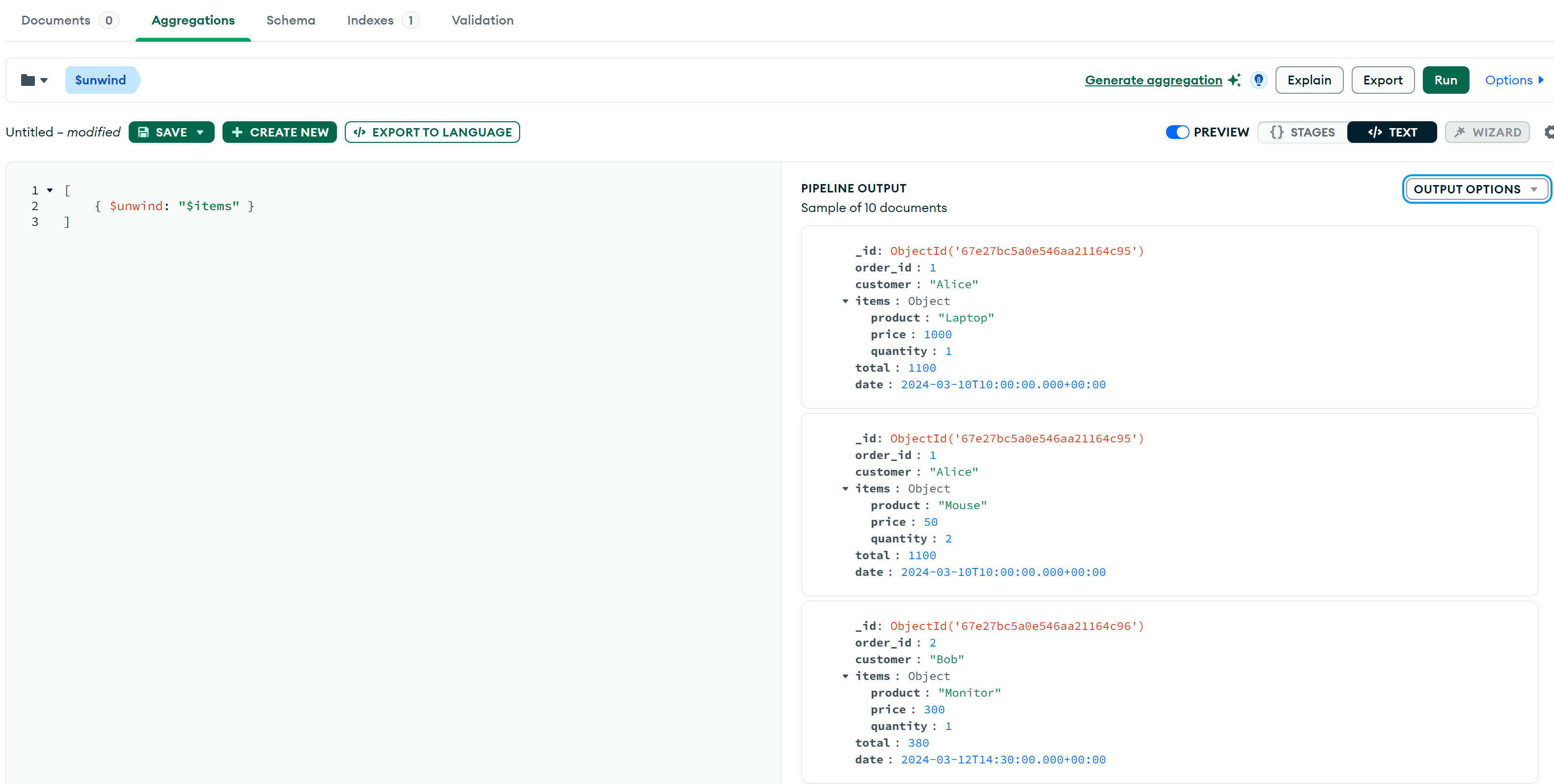
}$unwind
展开 items
数组,使每个订单的每个商品成为单独的文档:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $unwind: "$items" }
]);部分结果:
$lookup 连接另一集合
customers 集合包含客户的详细信息,我们可以使用
$lookup 进行关联查询,类似join:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
from: "customers",
localField: "customer",
foreignField: "name",
as: "customer_info"
}
}
]);部分结果,客户的详细信息已在customer_info:
{
"_id": {
"$oid": "67e27bc5a0e546aa21164c95"
},
"order_id": 1,
"customer": "Alice",
"items": [
{
"product": "Laptop",
"price": 1000,
"quantity": 1
},
{
"product": "Mouse",
"price": 50,
"quantity": 2
}
],
"total": 1100,
"date": {
"$date": "2024-03-10T10:00:00.000Z"
},
"customer_info": [
{
"_id": 1,
"name": "Alice",
"email": "alice@example.com",
"phone": "123-456-7890"
}
]
}综合示例
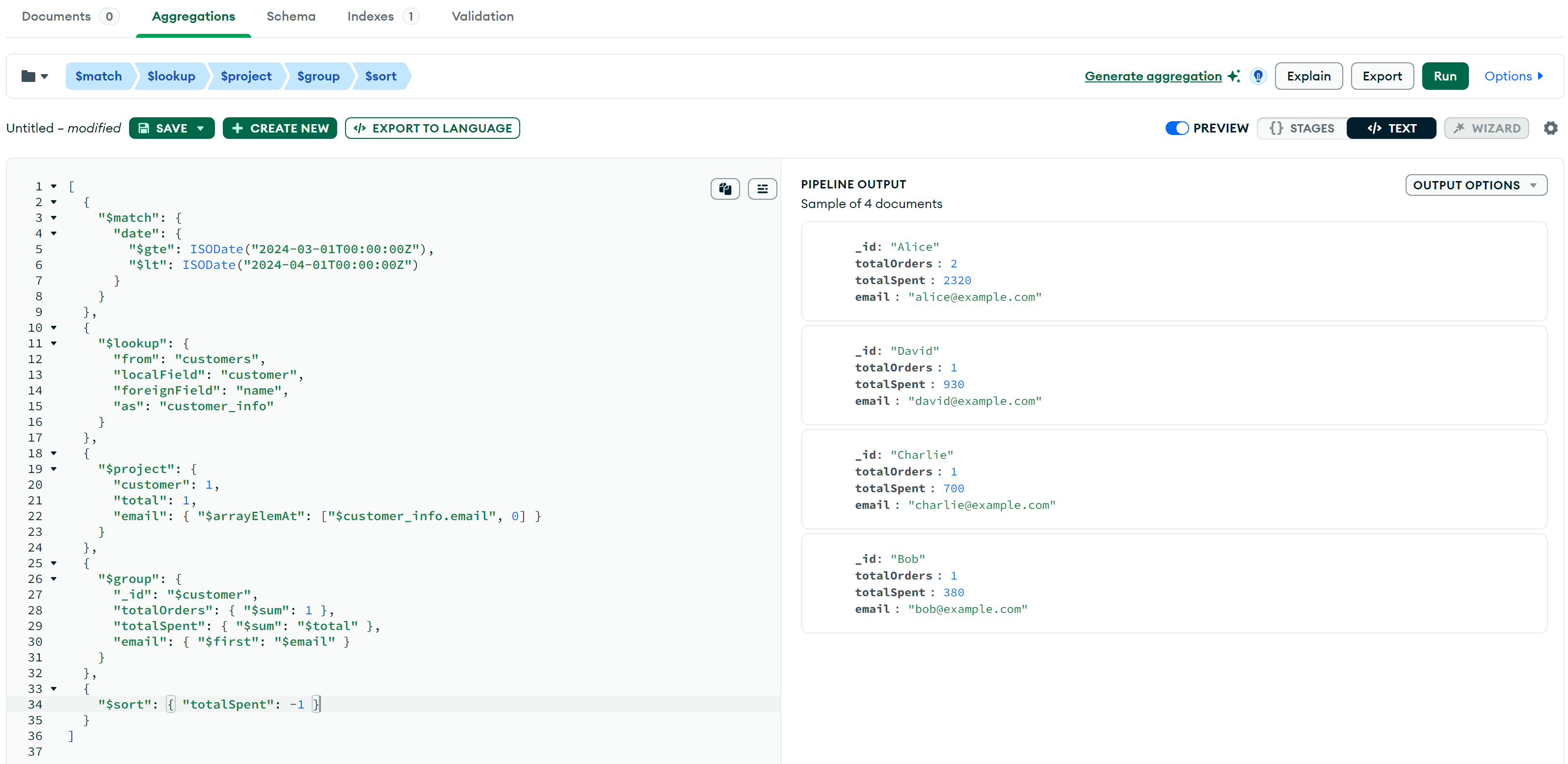
我们可以将多个阶段组合在一起,实现复杂的数据分析需求。例如,统计 2024 年 3 月 每个客户的订单总数和消费总额,同时获取客户的email,并按总消费金额降序排序:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
"$match": {
"date": {
"$gte": ISODate("2024-03-01T00:00:00Z"),
"$lt": ISODate("2024-04-01T00:00:00Z")
}
}
},
{
"$lookup": {
"from": "customers",
"localField": "customer",
"foreignField": "name",
"as": "customer_info"
}
},
{
"$project": {
"customer": 1,
"total": 1,
"email": { "$arrayElemAt": ["$customer_info.email", 0] }
}
},
{
"$group": {
"_id": "$customer",
"totalOrders": { "$sum": 1 },
"totalSpent": { "$sum": "$total" },
"email": { "$first": "$email" }
}
},
{
"$sort": { "totalSpent": -1 }
}
]);结果如下:
Aggregation Pipeline 性能分析与优化
性能分析
分析 Aggregation Pipeline 性能的方法包括:
explain()诊断:使用db.collection.aggregate([...]).explain("executionStats")来分析查询计划,检查索引使用情况和每个阶段的执行情况。profiler:启用 MongoDB Profiler (db.setProfilingLevel(2)) 记录慢查询,并分析system.profile集合。行时间。- MongoDB Atlas Performance Advisor(如果使用 Atlas):提供自动优化建议。
性能优化
一般而言,Aggregation的性能受以下因素影响:
- 索引使用:
$match阶段应尽量利用索引,以减少扫描数据量。 - 阶段顺序:将
$match放在最前面,以减少后续计算。 - 数据量:处理大规模数据时,Pipeline 可能占用大量内存。
索引优化
确保 $match 使用索引,提高查询效率。例如:
db.orders.createIndex({ "status": 1, "createdAt": -1 })减少 $lookup 依赖
$lookup 可能导致性能下降,一些优化方案如:
- 预处理数据,避免运行时
JOIN - 使用嵌套文档存储相关数据
Pipeline 阶段顺序优化
最佳顺序:
$match- 先过滤数据,减少后续处理量。$project- 去除不必要的字段,降低开销。$sort- 适当使用索引排序,避免内存消耗。$group- 仅在必要时聚合。
MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline 提供了强大的数据处理能力,适用于数据分析、ETL 及离线任务。通过合理使用索引、优化 Pipeline 结构和采用分片技术,可以显著提高性能。