Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models简读
# Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models
一篇实验Paper,调研了神经网络语言模型交叉熵损失变化满足power-law定律,挺有意思的文章。Transformer之后有许多探索不同模型结构的文章,并在一些任务上取得了新的SOTA,却鲜有人考虑影响模型性能的主要因素是什么。
Throughout we will observe precise power-law scalings for performance as a function of training time, context length, dataset size, model size, and compute budget.
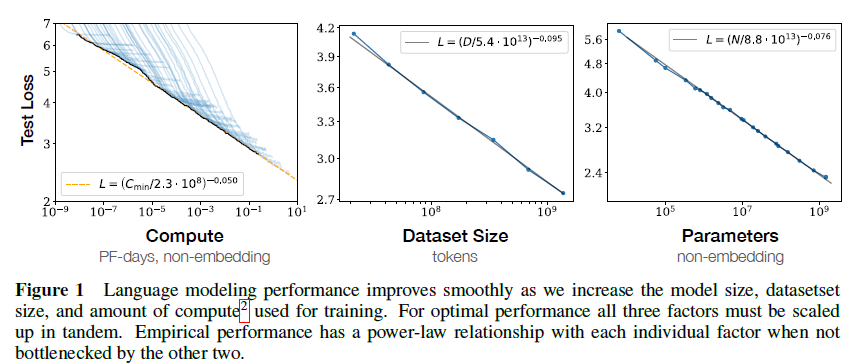
该文主要建模了模型性能与非embedding参数 N,数据集大小 D 与计算量 C之间的关系。最主要的发现:
- 性能主要与模型大小相关,而与模型结构弱相关
- 性能与上面三个因素有比较贴合的power-law关系
从实验来看,模型越大越好,小模型确实达不到大模型大力出奇迹的效果,而模型结构也并没有那么重要(虽然有很多工作是在改进模型结构本身)。
结论部分更强调了大模型比大数据更重要:
Our results strongly suggest that larger models will continue to perform better, and will also be much more sample efficient than has been previously appreciated. Big models may be more important than big data.